How to Increase Egg Quality for a Healthy Pregnancy
Age affects egg quality, and lifestyle, diet, and medical conditions also play a role. The good news? There are natural and medical ways to support and improve it. Let's explore what affects egg quality and how you can enhance it to boost fertility and improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
What Does "Egg Quality" Mean?
Every month during ovulation, a woman releases an egg. If that egg is fertilized by sperm, it forms an embryo. But for the embryo to grow properly, the egg needs to be healthy. A good-quality egg can lead to successful fertilization, healthy embryo formation, and a full-term pregnancy.
On the other hand, a poor-quality egg may have damaged or abnormal chromosomes. This can lead to several problems, such as:
- The egg not getting fertilized
- An embryo that doesn’t grow or implant properly
- A higher risk of miscarriage
- A failed IVF or ICSI cycle
It’s important to understand that egg quantity and egg quality are not the same. A woman may have many eggs, but if the quality is low, chances of conception may still be reduced.
Improving egg quality is possible in many cases with lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, supplements, and medical support. Focusing on egg health is an important step toward boosting fertility and increasing the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Why Is Egg Quality Important for Pregnancy?
High-quality eggs have normal chromosomes, which reduces the chances of embryo implantation failure or pregnancy loss. Chromosomal abnormalities in the egg are a major cause of early miscarriages, especially in women over 35.
Moreover, good egg quality supports proper embryo development, leading to higher chances of successful implantation in the uterus and the growth of a healthy fetus. In IVF cycles, the quality of the egg directly affects the quality of the embryos, which in turn influences the success rate of the treatment.
When egg quality is compromised, even the most advanced fertility treatments may not yield positive results. That’s why fertility specialists emphasize strategies to optimize egg health, especially in women with conditions like diminished ovarian reserve, PCOS, or advancing age.
In essence, egg quality is the foundation of a healthy pregnancy. It determines not just whether an egg can be fertilized, but also whether it can sustain normal development, implantation, and birth. Taking steps to enhance egg quality can significantly increase the chances of natural conception or IVF success.
Factors That Affect Egg Quality
1. Age & Egg Quality
Age is the most significant factor affecting egg quality. Women are born with a fixed number of eggs, and both egg quantity and quality naturally decline over time. After the age of 35, the decline becomes more rapid, and the risk of eggs carrying chromosomal abnormalities increases significantly. By the early 40s, many women face challenges with conception due to diminished ovarian reserve and poorer egg quality, even if they still have regular menstrual cycles.
2. Lifestyle & Environmental Factors
Everyday lifestyle choices can have a profound impact on fertility. Smoking, excessive alcohol, and high caffeine intake are known to damage the DNA in eggs and reduce their viability. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and being under or overweight can also contribute to hormonal imbalances that negatively affect egg development.
Environmental exposures—such as air pollution, pesticides, heavy metals, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) found in plastics and household products—can accumulate in the body over time and interfere with ovarian function. These toxins can impair the mitochondrial function of eggs, leading to a decline in both energy levels and genetic integrity.
3. Medical Conditions & Hormonal Imbalances
Certain health conditions can directly or indirectly impair egg quality. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid dysfunction, and insulin resistance are common culprits that disrupt hormonal balance and ovulation. Chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and persistent stress can also alter the internal environment of the ovaries, making it less conducive for healthy egg maturation.
Addressing these factors early through lifestyle modifications, medical management, and regular fertility check-ups can go a long way in preserving and improving egg quality.
Natural Ways to Improve Egg Quality
A balanced and nutrient-rich diet plays a crucial role in nourishing your eggs and improving overall fertility. The food you eat can support hormone balance, reduce oxidative stress, and create a healthy internal environment for egg development.
1. Fertility-Boosting Foods
- Healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E, both of which help improve ovarian function and reduce inflammation.
- Leafy greens (like spinach, kale, and broccoli) and colorful vegetables (like bell peppers and carrots) are loaded with antioxidants, which help protect eggs from free radical damage.
- Lean proteins such as eggs, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu supply essential amino acids that support hormone production and egg development.
- Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and quinoa provide complex carbohydrates and B vitamins, helping maintain stable blood sugar and hormonal balance.
- Processed foods, sugary snacks, and refined carbs increase inflammation and oxidative stress, which can damage egg cells.
- High caffeine intake (more than 200 mg/day) and alcohol consumption are linked to hormonal disruption and reduced fertility.
- Avoid trans fats and excess red meat, as they may negatively impact ovulatory function.
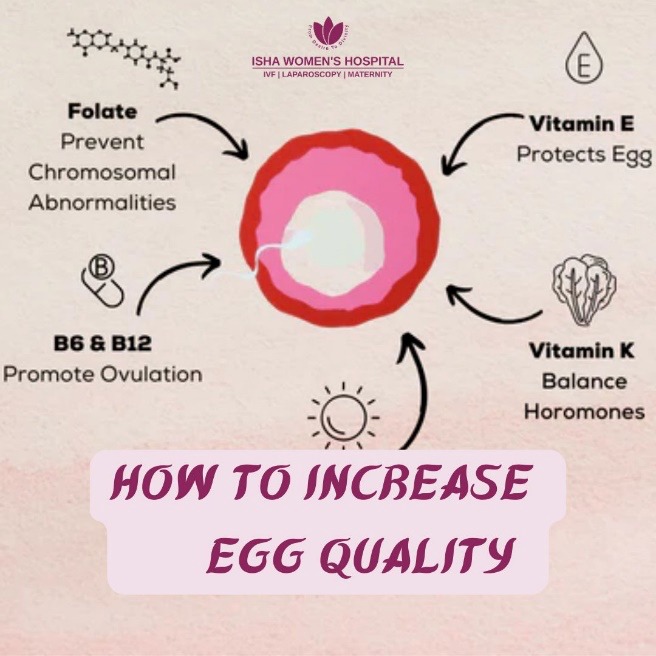
Key Supplements for Egg Health
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant that plays a vital role in mitochondrial function—the energy powerhouse of the egg cell. It enhances energy levels within the egg, improving fertilization and embryo development, especially in women over 35.
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone): DHEA is a hormone precursor that may help women with diminished ovarian reserve. It supports the development of more high-quality eggs and can improve IVF success rates when taken under medical supervision.
- Vitamin D: This essential nutrient regulates reproductive hormones and plays a key role in the health of the endometrium and ovarian function. Many women of reproductive age are deficient in vitamin D, which may impair fertility.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, omega-3s reduce inflammation, regulate hormones, and support blood flow to the reproductive organs.
- Folate and B Vitamins (B6 & B12): These are critical for DNA synthesis and repair, which is essential for egg health. Folate also reduces the risk of neural tube defects during pregnancy.
Exercise & Egg Quality: What Works Best?
- Engaging in moderate, consistent exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces inflammation, and improves insulin sensitivity—all of which support hormonal balance and ovarian function. Activities such as brisk walking, yoga, swimming, and light strength training are ideal for enhancing fertility.
- Yoga in particular offers dual benefits: physical activity and stress reduction. It improves blood flow to the reproductive organs, promotes relaxation, and supports endocrine health, making it a fertility-friendly choice.
- However, excessive or intense exercise—like marathon running or high-impact interval training—can disrupt ovulation and lower progesterone levels, especially in women with low body fat. Over-exercising can lead to hypothalamic amenorrhea, where the menstrual cycle becomes irregular or stops altogether.
Remember, when it comes to fertility, more isn’t always better. A gentle and consistent approach to movement will help create the ideal hormonal environment for high-quality eggs.
How Sleep & Stress Impact Egg Health
The Impact of Sleep
During sleep, the body undergoes critical hormonal regulation. Inadequate sleep (less than 6 hours per night) can disrupt melatonin and cortisol levels, leading to irregular ovulation and hormonal imbalance. Melatonin, commonly known for regulating sleep cycles, also protects eggs from oxidative stress.
Women who consistently get 7–9 hours of quality sleep have been shown to have better reproductive outcomes and hormonal stability.
The Role of Stress
Chronic stress leads to elevated cortisol levels, which negatively affect the production of reproductive hormones like estrogen and progesterone. It can also interfere with ovulation and reduce libido.
Stress doesn’t just affect the mind—it also impacts the physical environment of the ovaries, making it harder for eggs to mature properly.
Managing Stress for Fertility
Practicing mind-body techniques like meditation, deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, journaling, and acupuncture can significantly reduce stress hormones and improve egg quality. Regular physical activity and a strong social support system also help manage emotional well-being.
Creating a calming evening routine, limiting screen time, and prioritizing rest are essential for fertility wellness. A calm, rested body is better able to nurture and release healthy eggs.
Medical & Advanced Fertility Treatments and PRP Therapy & Other Medical Advances
For women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF), egg quality plays a crucial role in determining the success of the treatment. Thankfully, targeted lifestyle changes and medical strategies can help improve outcomes.
Before starting an IVF cycle, fertility specialists often recommend pre-IVF supplementation. Key supplements like CoQ10, DHEA, Omega-3s, and folate to support mitochondrial function, DNA repair, and hormonal balance, enhancing egg development and embryo quality.
Adopting a fertility-friendly lifestyle is equally important. A balanced diet, stress management, regular moderate exercise, and adequate sleep all contribute to a healthier reproductive system. Avoiding smoking, excessive caffeine, alcohol, and environmental toxins is critical for optimizing IVF success.
Women with low ovarian reserve or poor egg quality may benefit from personalized fertility treatment protocols, such as tailored medication dosages, natural or mild IVF cycles, or dual stimulation protocols.
Some women also explore adjunctive therapies like acupuncture, antioxidant infusions, or growth hormone supplementation as part of their IVF journey.
By combining medical insight with proactive lifestyle choices, many women are able to boost egg quality and improve their chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy through IVF.
PRP Therapy & Other Medical Advances
Recent advancements in reproductive medicine are opening new doors for women struggling with poor egg quality or age-related infertility. One promising innovation is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy.
PRP therapy involves extracting a sample of the patient's own blood, concentrating the platelets, and injecting them into the ovaries. These platelets are rich in growth factors that may stimulate the regeneration of ovarian tissue, enhance follicle development, and potentially improve egg quality. While still considered experimental, early studies show encouraging results, particularly in women with diminished ovarian reserve or undergoing early menopause.
In addition to PRP, Acupuncture is gaining popularity as a complementary therapy in fertility treatment. By improving blood flow to the ovaries and uterus, reducing stress, and balancing hormones, acupuncture may enhance the body’s response to IVF or other fertility interventions.
Some women also explore traditional medicine approaches, such as Ayurveda, Chinese herbal medicine, or homeopathy, alongside conventional treatments. While these therapies should always be used under professional guidance, they can support overall wellness and reproductive health.
As medical science continues to evolve, integrating innovative and holistic approaches offers new hope for improving egg quality and achieving a successful pregnancy.
When to See a Fertility Specialist
If you’re under 35 and have been trying to conceive for more than 12 months, or over 35 and trying for more than 6 months, it’s time to consult a fertility specialist. Early intervention can make a significant difference, especially if egg quality or quantity is declining.
You should also consider seeing a specialist if you have:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
- A diagnosis of PCOS, thyroid issues, or endometriosis
- A history of repeated miscarriages
- Previous pelvic surgery or infections
- A known family history of early menopause
Don’t let time or uncertainty stand in your way—take charge of your reproductive health today. Schedule your consultation and move forward with confidence toward the dream of parenthood.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Ans - It takes 3-4 months to improve egg health.
2. Does folic acid improve egg quality?
Ans - Yes! Folate & B vitamins support DNA integrity in eggs.
3. Can stress affect egg quality?
Ans - Yes, chronic stress increases cortisol, impacting fertility.
4. Can I improve egg quality after 40?
Ans - Yes! Supplements, diet, and medical treatments can help.
5. What are the best fertility-boosting foods?
Ans - Leafy greens, nuts, salmon, whole grains, and avocado.
